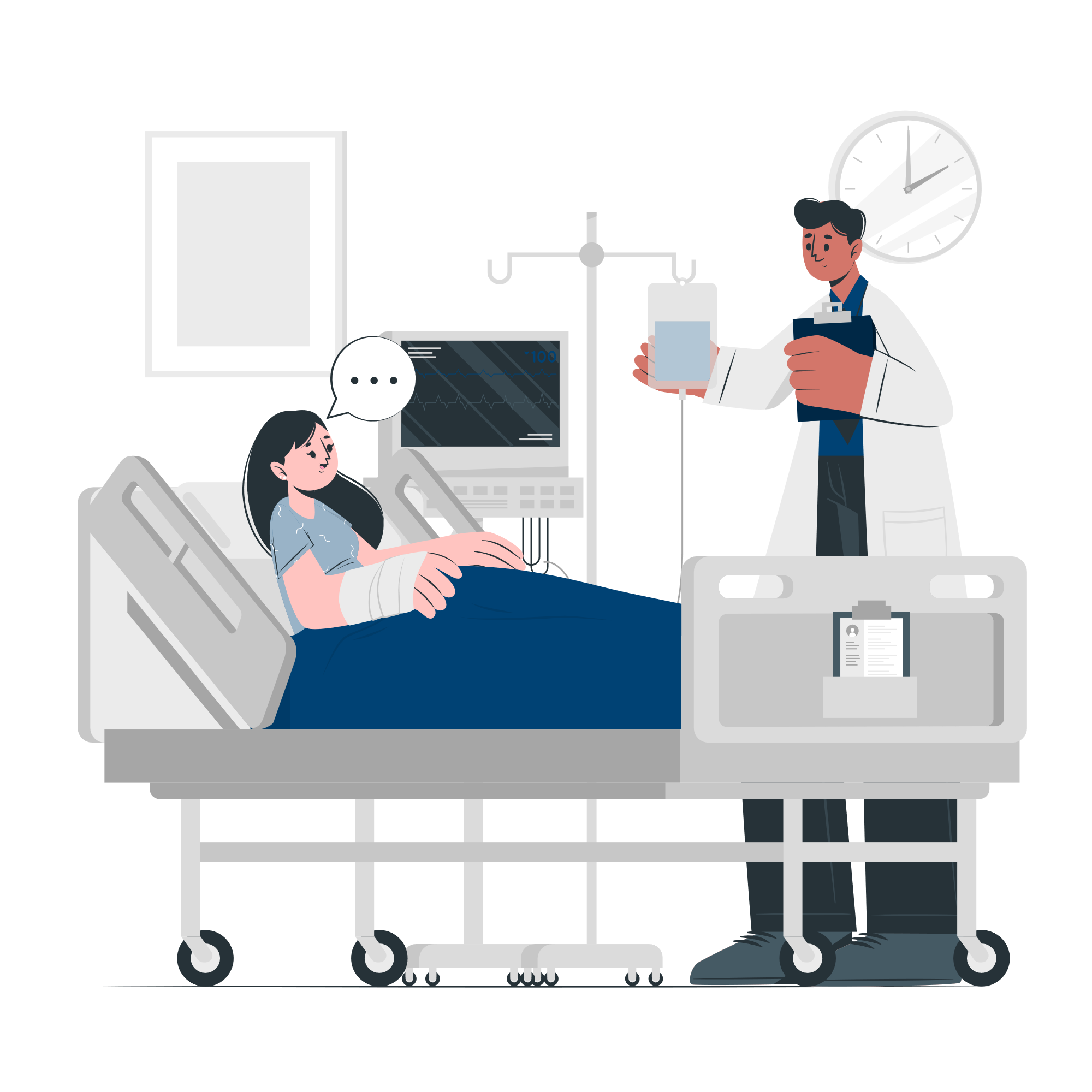

CRRT Dialysis
What is CRRT Dialysis ?
Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy (CRRT) is a 24-hour non-stop dialysis therapy used to support patients with renal (kidney) failure.
CRRT gently filters and cleans your child’s blood. Your child will need a special intravenous (IV) catheter in one of his or her large veins (usually in the neck or groin) for this treatment. The blood is removed from the body through the IV and sent through the CRRT machine. The blood is pumped through the filter, which cleans it and returns it to the body.
CRRT is needed when the kidneys are no longer able to remove enough waste and water from the blood. In this case, your child may need CRRT until the kidneys begin to work again. CRRT works like the kidneys to remove harmful waste and fluid. This helps keep the right balance of chemicals and electrolytes, like potassium and sodium, in your child’s blood. CRRT does the work of the kidneys while your child’s kidneys are trying to heal and get better.


Hematology
What is hematology?
Hematology is the study of blood and blood disorders. Hematologists and hematopathologists are highly trained healthcare providers who specialize in diseases of the blood and blood components. These include blood and bone marrow cells. Hematological tests can help diagnose anemia, infection, hemophilia, blood-clotting disorders, and leukemia.


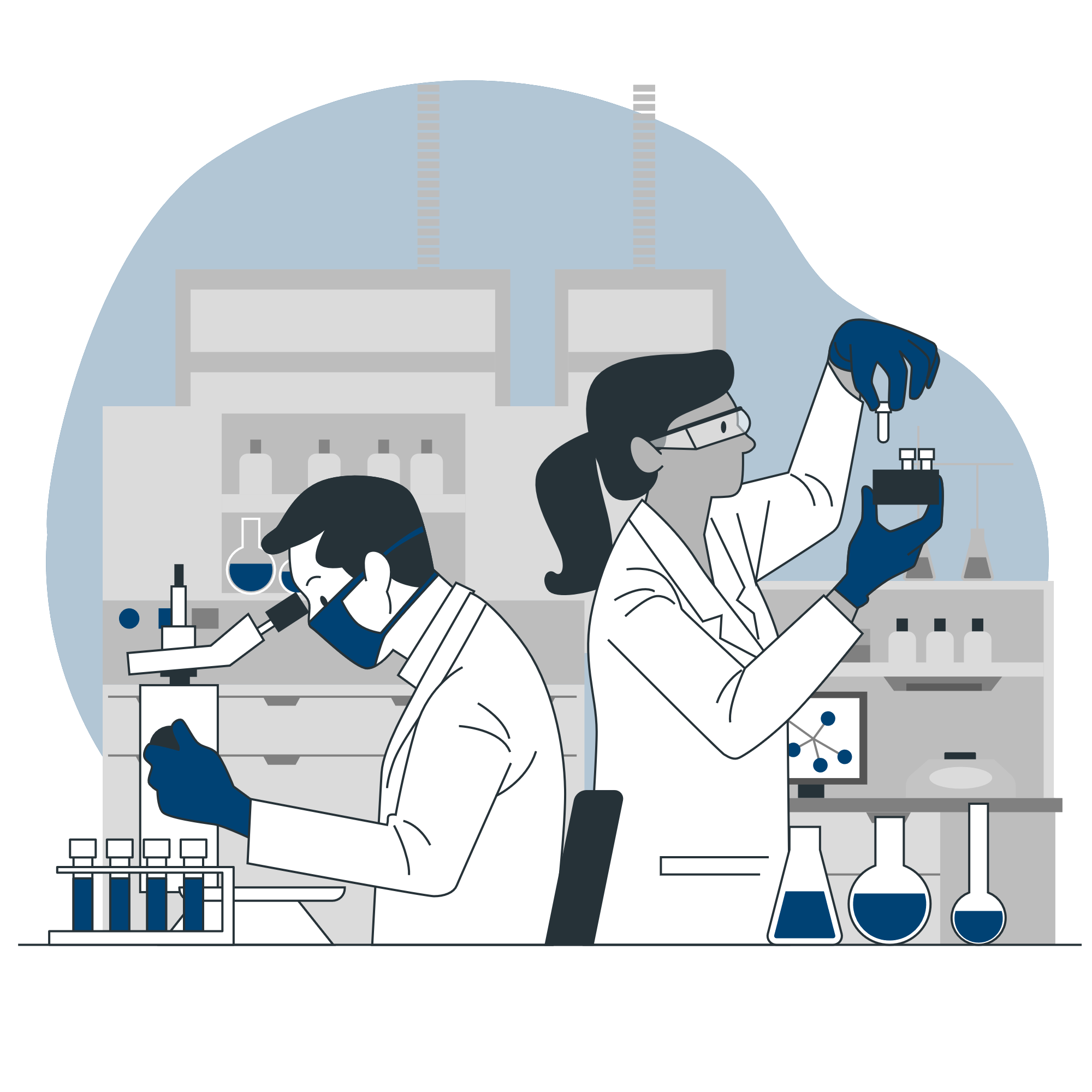
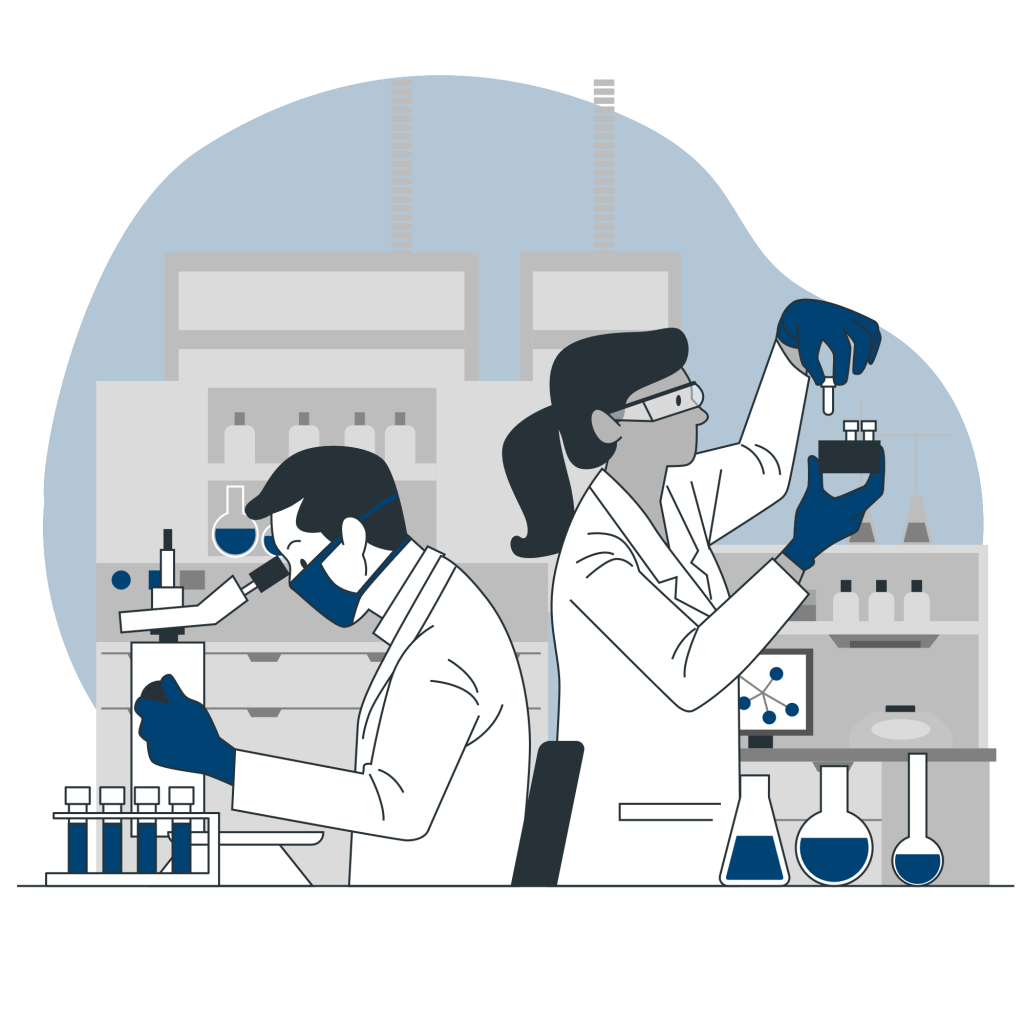
Laboratory
What is Laboratory?
A laboratory is a facility that provides controlled conditions in which scientific or technological research, experiments, and measurement may be performed. Laboratory services are provided in a variety of settings: physicians’ offices, clinics, hospitals, and regional and national referral centers.
The role of a clinical laboratory is to promptly provide highly reliable laboratory data to satisfy the needs of clinicians involved in medical practice and health maintenance of patients. Improvement and maintenance of the quality of the laboratory staff and environment are essential to achieve this goal.


Maternity & Women’s Health
What is Maternity & Women’s Health ?
Women’s health includes a wide range of specialties and focus areas, such as: Birth control, sexually transmitted infections (STIs), and gynecology. Breast cancer, ovarian cancer, and other female cancers. Mammography.
A child cannot be healthy or happy absent the presence of a healthy and happy mother. Prenatal and postpartum maternal health is critical to a mother’s physical and mental well-being and contributes to her ability to render loving, proper care to her newborn child at birth and years thereafter.
Maternal and child health is an important public health issue because: * we have the opportunity to end preventable deaths among all women, children and adolescents and to greatly improve their health and well-being.


Mental & Behavioral Health
What is Mental & Behavioral Health?
Mental health includes our emotional, psychological, and social well-being. It affects how we think, feel, and act. It also helps determine how we handle stress, relate to others, and make choices. Mental health is important at every stage of life, from childhood and adolescence through adulthood.
Behavioral health is the way your habits impact your mental and physical wellbeing. That includes factors like eating and drinking habits, exercise, and addictive behavior patterns. Substance abuse, eating disorders, gambling and sex addiction are all examples of behavioral health disorders.
It is a term that falls under the general umbrella of behavioral health, but it’s much broader than just a person’s behaviors. While behavioral health refers to how behaviors impact an individual’s well-being, mental health is primarily concerned with the individual’s state of being.


Peritoneal Dialysis
What is Peritoneal Dialysis?
Peritoneal dialysis is a way to remove waste products from your blood when your kidneys can’t adequately do the job any longer. This procedure filters the blood in a different way than does the more common blood-filtering procedure called hemodialysis.
Mortality rates have fallen over the past several years, but long-term survival remains poor, with only 11% of peritoneal dialysis patients surviving past 10 years. Cardiovascular disease accounts for most deaths, and dialysis patients have many traditional and nontraditional cardiovascular risk factors.


Primary Care
What is Primary Care?
Primary care is the provision of integrated, accessible health care services by physicians and their health care teams who are accountable for addressing a large majority of personal health care needs, developing a sustained partnership with patients, and practicing in the context of family and community.
Your primary healthcare practitioner is usually your regular GP, who provides comprehensive and ongoing general medical care, but you may have several primary health professionals you see regularly. For example, a dentist, counsellor, dietitian, osteopath or physiotherapist, are all primary healthcare providers.
Primary care is the main doctor that treats your health, usually a general practitioner or internist. Secondary care refers to specialists. Tertiary care refers to highly specialized equipment and care.
Radiology
What is Radiology?
Radiology is a branch of medicine that uses imaging technology to diagnose and treat disease. Radiology may be divided into two different areas, diagnostic radiology and interventional radiology. Doctors who specialize in radiology are called radiologists.
X-ray, or radiography, is used to diagnose fractured bones, detect injury or infection, or to locate foreign objects in soft tissue. Some x-ray exams employ an iodine-based contrast material to clarify the visibility of specific organs like the heart, lungs, blood vessels or tissues.
What happens during radiology?
Radiologists are doctors who take pictures of the inside of your body to help diagnose and treat illnesses. These medical images are taken in different ways, including: X-ray. CT scan (multiple, computerized X-rays)
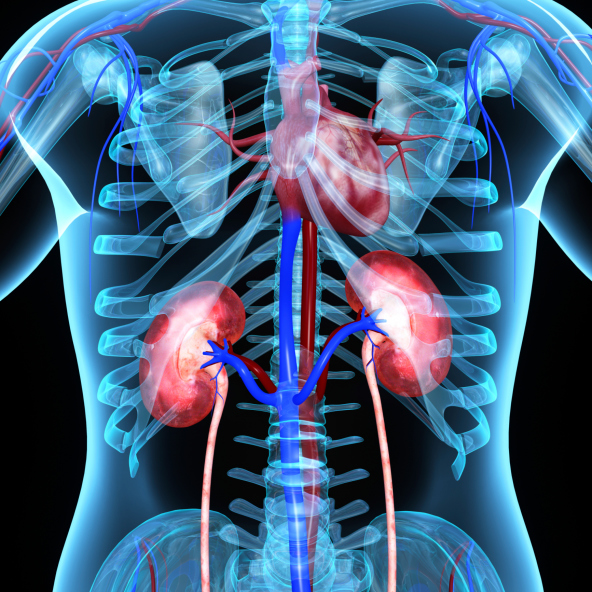
Renal & Cardiovascular
What is Renal & Cardiovascular?
When the kidneys don’t work well, more stress is put on the heart. When someone has CKD, their heart needs to pump harder to get blood to the kidneys. This can lead to heart disease, the leading cause of death in the United States. Change in blood pressure is also a CKD complication that can lead to heart disease.
Relatively recent research has shown that heart failure is a significant risk factor for kidney disease. When the heart is no longer pumping efficiently it becomes congested with blood, causing pressure to build up in the main vein connected to the kidneys and leading to congestion of blood in the kidneys, too.
Urinary system and Circulatory systems work together: The urinary system cleans the blood in the circulatory system. Blood traveling back to the heart passes through the kidneys in the urinary system. The kidneys clean the blood and control the amount of salt, water, and other substances in the blood.
Hemodialysis
What is Hemodialysis ?
Hemodialysis is a procedure where a dialysis machine and a special filter called an artificial kidney, or a dialyzer, are used to clean your blood. To get your blood into the dialyzer, the doctor needs to make an access, or entrance, into your blood vessels. This is done with minor surgery, usually to your arm.
The dialyzer, or filter, has two parts, one for your blood and one for a washing fluid called dialysate. A thin membrane separates these two parts. Blood cells, protein and other important things remain in your blood because they are too big to pass through the membrane. Smaller waste products in the blood, such as urea, creatinine, potassium and extra fluid pass through the membrane and are washed away.
Hemodialysis can be done in a hospital, in a dialysis center that is not part of a hospital or at home. You and your doctor will decide which place is best, based on your medical condition, and your wishes.
